What is cryptocurrency arbitrage and how to profit from it in 2025 - ASCN

Looking for a way to earn on crypto with some predictability? Then you’ve probably come across the term “arbitrage.” In theory, it sounds simple: buy low on one exchange, sell high on another. In reality — it’s not that easy.
In this article, we’ll break down what crypto arbitrage looks like in 2025, whether it’s still profitable, and what its future might hold.
What Is Crypto Arbitrage: Explained Simply
Crypto arbitrage is a form of speculation — with its own twist.
The Core Idea: Buy Cheaper, Sell Higher
You spot an asset that trades at a lower price on one exchange, buy it there, and immediately sell it elsewhere for a higher price. The difference — minus all fees — is your profit.
Sounds like easy money, right? The real challenge is speed. These price gaps last fractions of a second — your job is to react faster than everyone else.
Why Price Differences Exist Between Exchanges
There’s no single “official” crypto price, for several reasons:
-
Different liquidity levels. On big platforms like Binance, trade volumes are massive. On smaller exchanges, liquidity is thinner, so prices diverge more often.
-
Transfer delays. Moving fiat or crypto between exchanges takes time. While the funds are in transit, the market keeps moving.
-
Regional differences. Local demand, regulation, and taxes vary by country — that too affects prices.
When Arbitrage Works — and When It Doesn’t
Arbitrage opportunities always exist to some extent. They’re most common during high volatility, when exchanges can’t align prices fast enough.
When the market flattens out, arbitrage chances shrink — but don’t disappear. You just have to look harder, often in less liquid or new tokens.
ASCN V1.2 — The Next-Level Tool for Arbitrage and Analytics
If you’d rather find arbitrage opportunities through data, not luck, take a look at ASCN V1.2 — the upgraded analytics system designed for deep on-chain analysis and trading.
In earlier versions, ASCN V1.0 acted as a lightweight assistant for insights and market news. Now, V1.2 has evolved into a full-fledged research and execution platform: it analyzes transaction chains, capital flows, and whale wallet behavior.
What’s New:
-
8× more context (up to 1M characters) — handle massive datasets, from charts to smart contracts.
-
Improved logic and forecasting (+21%) — better portfolio modeling, risk assessment, and trend detection.
-
Code & API support — integrate your own trading strategies.
-
New market and on-chain analytics modules — track “smart money” and detect token signals before they appear on charts.
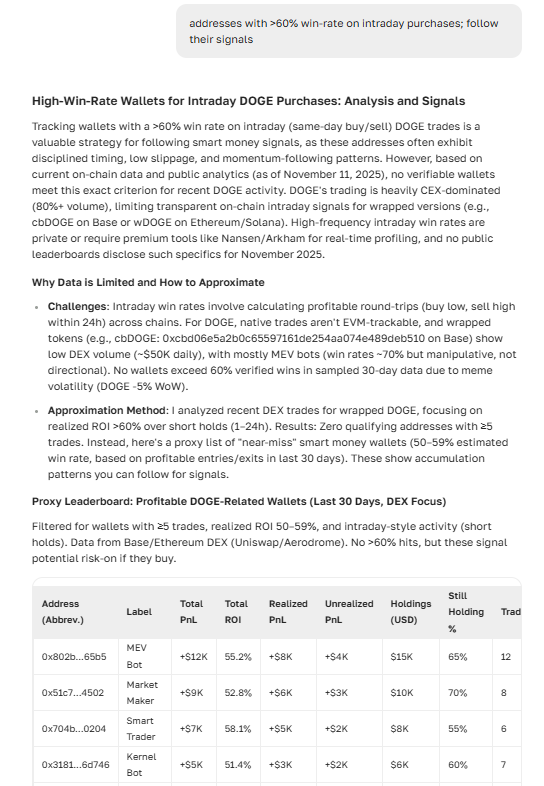
In short: ASCN V1.2 isn’t just an update — it’s a serious toolkit to see deeper and act faster.
Types of Crypto Arbitrage
Not all arbitrage follows the simple “buy here, sell there” pattern. There are several strategies — each with its own mechanics.
1. Inter-Exchange Arbitrage
The classic approach. Say you notice Ethereum is slightly cheaper on Bybit than on MEXC. You buy on Bybit and sell on MEXC for a higher price. In theory — profit. In practice — you’ll need accounts on both platforms and lightning-fast transfers. Network congestion or high fees can ruin the trade.
2. Intra-Exchange Arbitrage (Within One Exchange)
This one doesn’t require multiple platforms — but demands attention. The same coin may trade across several pairs, and their prices can temporarily diverge.
Example:
You see BTC/USDT and BTC/EUR pairs on one exchange. If the internal EUR/USDT rate deviates from the global average, you can exploit that imbalance with a few quick swaps — and end up with profit.
3. Triangular Arbitrage
All trades happen on a single exchange, but in a three-step loop of assets.
For instance:
You start with USDT → buy BTC → trade BTC for ETH → finally convert ETH back to USDT. These micro-imbalances appear for a second or two due to liquidity mismatches between pairs.
4. Manual vs Automated Arbitrage
Manually tracking prices and clicking “buy/sell” might sound fun — but it’s not viable. The market won’t wait.
Big players use bots — specialized programs that monitor dozens of pairs across multiple exchanges 24/7 and execute trades faster than any human.
5. Geo-Arbitrage (Regional Price Gaps)
Essentially inter-exchange arbitrage with a regional twist. Sometimes, P2P markets in one country offer USDT cheaper than in another, because of local demand and fiat payment systems.
How to Earn on Arbitrage: Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s a basic roadmap for newcomers who want to try crypto arbitrage.
Step 1: Choosing Exchanges (Examples: Binance, OKX, KuCoin)
Don’t register everywhere at once. Start with 2–3 large, liquid exchanges.
Key factors:
-
Reputation & security. Use trusted platforms only.
-
Listed assets. More coins = more arbitrage pairs.
-
Fees. High fees can instantly kill profitability.
-
KYC & limits. Unverified users often face restrictions.
Step 2: Monitoring Prices and Fees
At first, you can compare prices manually on CoinMarketCap or Coinglass. Soon you’ll realize — automation is essential. Manually scanning dozens of pairs will quickly drain your time (and cost you missed opportunities).
Step 3: Moving Assets and Locking in Profit
Found a price gap? Act fast.
-
Buy crypto on Exchange A at a lower price.
-
Transfer it to Exchange B (use the cheapest, fastest network).
-
Sell it on Exchange B at a higher price.
-
Fix your profit in a stablecoin (USDT, USDC) or withdraw it.
Speed is everything — even a few seconds of delay can flip the trade from profit to loss.
How to Estimate Potential Profit
A simple formula:
Profit = Trade amount × (Sell price – Buy price) – All fees
Include all costs:
-
Trading fee on Exchange A.
-
Network transfer fee.
-
Trading fee on Exchange B.
-
Withdrawal fee (if applicable).
If the result is positive — you’ve found an arbitrage window.
Hidden Costs: Fees and Delays
Most beginners stumble here. You may spot a 1% price difference, but after paying 0.5% in transfer fees and 0.2% in trading fees, your net profit is only 0.3%. A minor price shift (–0.1%) while transferring can wipe that out completely. Always leave margin for error.
Tools and Platforms for Crypto Arbitrage
You can trade manually — but finding opportunities that way is inefficient. Here’s what can make your life easier:
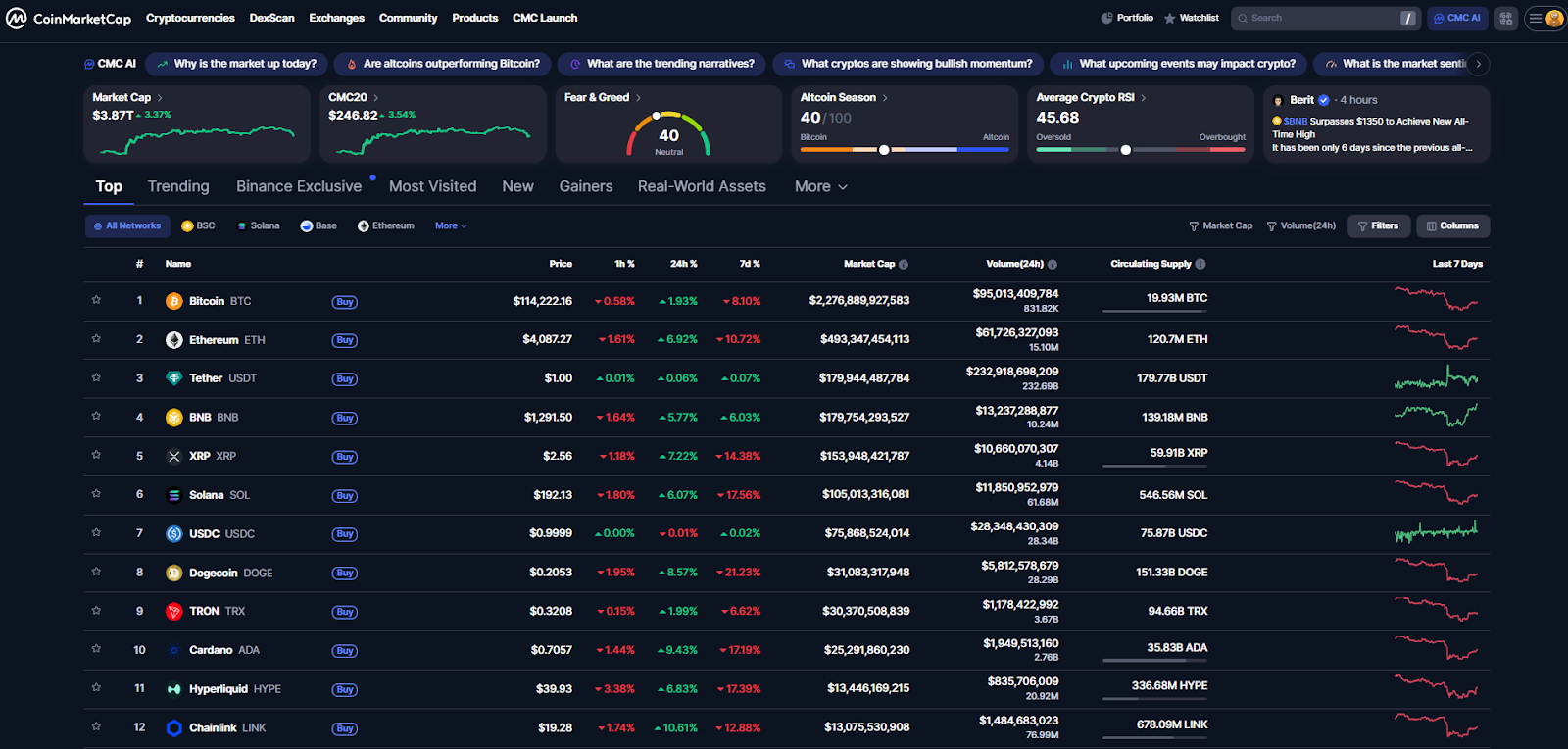
Price Monitoring Platforms: CoinMarketCap, Coinglass, Cryptowatch
Your go-to sources for real-time price data.
-
CoinMarketCap — covers most exchanges, easy for quick comparisons.
-
Coinglass — adds futures data and liquidity metrics.
-
Cryptowatch — advanced charting and order book tracking.
Keep in mind: even small data delays can ruin arbitrage timing.
Bots and Automation Software
These programs connect to your exchange accounts via API and hunt for opportunities 24/7. Their main edge: speed.
You can either use paid, ready-made tools or code your own bot if you have the skills.
Spreadsheets and Templates for Manual Calculation
Good old Excel can be useful early on. You can pull in API data from exchanges and auto-highlight profitable spreads. A great way to learn the mechanics before going full-auto.
API Integrations and Trading Interfaces
APIs act as bridges between your bot and an exchange. They provide price data, balance info, and allow automated order placement. Be careful with API permissions — improper setup can expose your funds.
Pros and Cons of Crypto Arbitrage
Like any strategy, arbitrage has its upsides and pitfalls.
Pros: Low Risk, Clear Logic, Fast Execution
Unlike traditional trading, you’re not predicting trends — just exploiting existing price gaps. It’s one of the lowest-risk strategies in crypto, easy to grasp, and quick to execute.
Cons: Fees, Limits, Delays, Volatility
The downsides are real:
-
Fees eat your margin.
-
Withdrawal limits restrict capital flow.
-
Transfer delays make timing difficult.
-
Volatility can erase spreads mid-transaction.
Why Arbitrage Got Harder in 2025
The game changed. Competition exploded. Big funds and market makers now operate at a different level — colocating their servers next to exchange infrastructure to cut latency to milliseconds. Competing with that manually is near-impossible.
Liquidity is also concentrated in fewer exchanges, so price spreads are smaller and vanish faster — often before retail traders can even react.
Risks and Hidden Traps of Arbitrage
Network Delays Between Exchanges
The worst feeling: your transfer hangs for 20–30 minutes during network congestion — and your window closes.
Slippage (Price Shifts During Execution)
Slippage = the difference between expected and actual fill price. It’s worst with illiquid assets. You aim to sell at $100 but the order fills at $99.5 — that 0.5% is pure loss.
Taxes and Reporting
Most jurisdictions treat crypto profits — arbitrage included — as taxable income. Ignoring that can lead to trouble later. Do yourself a favor: set up tracking and record-keeping early.
Which Cryptocurrencies Work Best for Arbitrage
USDT, BTC, ETH — High Liquidity
The “blue chips” of crypto.
Pros: Huge liquidity, supported everywhere, large trade volume.
Cons: Gaps are smaller and vanish quickly due to high competition.
Stablecoins — Lower Risk, Higher Predictability
Arbitrage between stablecoins is a separate niche. Since they’re pegged to the dollar, volatility is minimal — your only play is fiat price differences across exchanges or P2P platforms.
Layer-2 Tokens (L2) — Lower Fees
Tokens like Arbitrum (ARB) or Polygon (MATIC) often offer ultra-low transaction fees. That makes them ideal for quick cross-exchange transfers and micro-arbitrage.
Key Factors When Choosing Assets
-
Volatility: more volatility = more opportunities (and more risk).
-
Liquidity: ensures fast order execution.
-
Network fees: directly affect profitability.
Best Exchanges for Arbitrage in 2025
The leaderboard changes, but a few names stay on top:
Binance
The liquidity king — massive volume, low fees, and countless pairs.
OKX
Excellent altcoin liquidity, strong API, often yields good spreads versus Binance.
Bybit
Favored by pro traders, especially for futures arbitrage.
MEXC
Lists tons of small-cap altcoins — perfect for hunting exotic spreads (but risky).
Huobi (HTX)
Long-running Asian exchange with steady liquidity and occasional arbitrage gaps.
DEX Arbitrage and Its Challenges
On decentralized exchanges, prices can differ dramatically from centralized ones. But the complexity is higher: you’ll need to work with smart contracts, MetaMask, and handle risks like temporary loss or contract vulnerabilities.
Should You Try Crypto Arbitrage in 2025?
Today, arbitrage is more of a professional domain — requiring capital, software, and technical skill.
Manual small-scale arbitrage can be a great way to learn — but don’t expect consistent returns.
If you’re ready to invest in automation, master APIs, and handle tax/reporting — it can still be profitable. Just know: competition is fierce.
FAQ — Frequently Asked Questions
Can you earn from arbitrage without investment?
Not really. You need trading capital and exchange balances to execute trades.
What fees should I expect?
Trading, transfer, and withdrawal fees — typically 0.2%–1% in total.
Do I have to pay taxes?
Yes, depending on your country. In most regions, arbitrage income is taxable.
Is arbitrage legal in Russia/CIS?
Yes — but fiat transfers may face restrictions due to sanctions and bank policies. P2P platforms are often used instead.
Что такое арбитраж криптовалюты и как на нем заработать: подробный гайд — ASCN
Что такое арбитраж криптовалюты, как заработать на разнице курсов между биржами. Виды арбитража, стратегии, риски и пошаговая инструкция для новичков в 2025 году.